Doors are essential elements in every building, seamlessly blending functionality with design. They provide security, insulation, and privacy while enhancing the visual appeal of spaces. This comprehensive glossary explores door types, parts, comparisons, and installation, offering clear answers to common questions. Whether you're a contractor, builder, or homeowner, you'll find practical insights to guide your decisions.
Table of Contents:
- Types of Doors
- Door Anatomy
- Comparison of Doors
- How to Choose a Door
- Door Maintenance
- Door Installation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Types of Doors
Below are the most common types of doors used in housing and construction projects.
Entry Doors
Entry doors, or exterior doors, are the focal point of a home’s exterior, offering a combination of style, security, and weather protection. They are built to withstand external elements while enhancing curb appeal.
- Materials: Common options include fiberglass, wooden doors, steel, and composite materials, each with unique advantages in durability and aesthetics.
- Locations: Installed where ever a plan calls for an entrances at a home or commercial building.
- When to Use: Choose entry doors to create a secure, inviting first impression while prioritizing energy efficiency and protection.
Entry Door Styles
- Contemporary Entry Doors: Featuring minimalist designs with bold colors and optional glass accents, these doors suit modern and urban aesthetics.
- Decorative Glass Entry Doors: Highlight intricate glass details, combining elegance with natural light. Perfect for traditional and transitional styles.
- Panel Entry Doors: Known for raised or recessed panels, these timeless designs fit classic to contemporary homes.
- Rustic Entry Doors: Featuring distressed wood or wood-look finishes, these doors complement farmhouse and cottage designs.
- Solid Wood Entry Doors: Durable and insulating, these doors bring warmth and character, ideal for traditional homes.
Patio Doors
Patio doors serve as a bridge between indoor and outdoor spaces, enhancing natural light and accessibility. Their expansive glass designs make them ideal for living areas connected to decks, patios, or gardens.
- Materials: Often crafted from glass, aluminum, fiberglass, or wood for durability and transparency.
- Locations: Used in rear-facing entrances to patios or backyards.
- When to Use: Perfect for homeowners who value aesthetic appeal and easy access to outdoor spaces. Configurations involving two doors, such as bifold doors or double door arrangements, are ideal for creating wide openings and enhancing the flow between indoor and outdoor areas.
Patio Door Styles
- Bi-Fold Patio Doors: Multiple panels fold accordion-style to create expansive openings and seamless indoor-outdoor transitions.
- French Patio Doors: Hinged panels swing open for a sophisticated and classic look, perfect for formal settings.
- Sliding Patio Doors: Sliding horizontally, they save space and maximize light, ideal for small or modern homes.
Interior Doors
Interior doors divide rooms, offer privacy, and contribute to the home’s decor. They come in various styles, materials, and finishes to suit functional and aesthetic needs.
- Materials: Available in solid core, hollow core, wood, and composite options to match performance requirements.
- Locations: Typically installed in bedrooms, bathrooms, offices, and closets.
- When to Use: Use interior doors to personalize spaces while addressing sound insulation and style considerations. Not all doors incorporate certain features, such as a middle rail or frieze rail, highlighting the diversity in door construction.
Interior Door Styles
- Swing Doors: The standard hinged door, versatile and suited for most rooms.
- Barn Doors: Sliding on tracks, they save space and add a rustic or modern aesthetic.
- Bifold Doors: Folding panels maximize space, often used in closets and pantries.
- Pocket Doors: Sliding into walls, these doors are perfect for compact spaces.
- French Doors: Elegant glass-paneled doors that allow light to pass between rooms.
- Louvered Doors: Featuring horizontal slats, they provide ventilation while maintaining privacy.
- Panel Doors: Classic raised or recessed designs suitable for various interiors.
Storm Doors
Storm doors provide an additional protective barrier for entry doors, improving insulation and ventilation. They enhance energy efficiency and preserve the lifespan of the primary door.
- Materials: Commonly made from aluminum, steel, or vinyl for weather resistance.
- Locations: Installed in front of exterior entry doors for added protection.
- When to Use: Ideal in regions with significant weather variations to shield doors from the elements. The exterior door frame, including components like the sill, plays a crucial role in preventing dirt and water ingress, further protecting the door structure.
Storm Door Styles
- Full-View Storm Doors: Large glass panels maximize visibility and light, often paired with interchangeable screens.
- Retractable Screen Storm Doors: Screens roll into the frame, offering ventilation without visual obstruction.
- Ventilating Storm Doors: Combines glass and screen panels for adjustable airflow and year-round functionality.
Door Anatomy: What Parts Make a Door?
- Frame: Supports the door structure and ensures proper alignment.
- Panel or Slab: The main body of the door, which may be decorative or solid.
- Threshold: The bottom component, designed for sealing and insulation. The bottom rail is a horizontal component that enhances the door's strength and provides a secure place for attaching hardware.
- Hinges: Allow doors to pivot open and closed securely.
- Locksets: The hardware components, including knobs, handles, and locking mechanisms, that secure the door.
- Jamb: The vertical parts of the door frame that house the hinges and locksets.
- Glazing: Glass elements, offering both style and natural light.
Door Components
Door Frame
A door frame is the essential structure that supports and secures the door, ensuring it operates smoothly and remains aligned. It consists of three main parts: the head (top horizontal component), the jambs (vertical sides), and the sill (bottom horizontal component).
Exterior door frames are particularly crucial as they provide protection against weather elements and enhance security. These frames can be crafted from various materials, including wood, aluminum, fiberglass, and composite materials, each offering different benefits in terms of durability and maintenance. Whether primed or factory-finished, exterior door frames come in a range of colors to match your home’s aesthetic.
Door Panel
The door panel, often referred to as a slab, is the main body of the door that swings open and closed. It can be a single solid piece or divided into smaller sections by stiles (vertical components), rails (horizontal components), and mullions (vertical or horizontal bars between panels).
Door panels are made from a variety of materials, such as wood, metal, and composite materials, each chosen for their specific properties like durability, insulation, and aesthetic appeal. Exterior door panels are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions while providing security and energy efficiency.
Door Jamb
The door jamb is a critical part of the door frame, consisting of the vertical sections on either side of the door opening. There are two side jambs and a head jamb, which is the top horizontal part. Together, these components form the supportive structure that holds the door in place.
Door jambs can be made from materials like wood, aluminum, fiberglass, and composite materials, chosen for their strength and resistance to wear. Properly installed door jambs ensure that the door operates smoothly and securely.
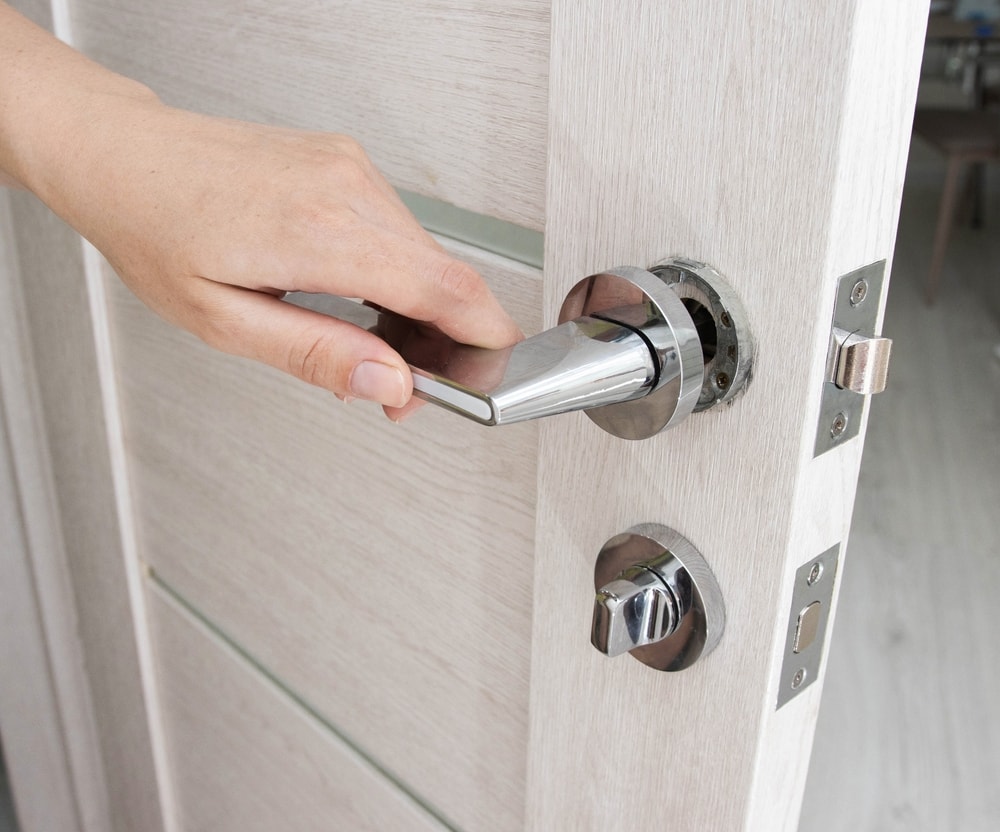
Door Hardware
Hinges
Hinges and locksets are vital components of door hardware, ensuring both functionality and security. Hinges are the metal parts that attach the door to the door frame, allowing it to pivot open and closed. They come in various styles and finishes to match the door’s design and ensure smooth operation.
Locksets
Locksets are the mechanisms that secure the door. A typical lockset includes a lock, latch, and strike plate. The lock stile is the vertical part of the door panel that houses the locking mechanism.
For added security, a metal plate installed on the door frame, known as a strike plate, reinforces the area where the latch engages, protecting against forced entry. Exterior door hardware is specifically designed to endure weather conditions while providing robust security and ease of use.
Door Comparison
Entry vs. Patio Doors
Entry doors excel in security, insulation, and curb appeal, often made of sturdy materials like steel or fiberglass. Patio doors, by contrast, emphasize functionality and natural light with glass-dominant designs. While entry doors protect and impress, patio doors connect and illuminate.
Solid Wood Doors vs. Hollow Core Doors
Solid wood doors offer unmatched durability, insulation, and elegance, suitable for premium interiors and exteriors. Hollow core doors are lightweight, affordable, and easy to install, making them ideal for low-traffic interior spaces. While solid wood doors excel in longevity, hollow core doors provide budget-friendly functionality.
Steel vs. Fiberglass Doors
Steel doors provide superior security and durability, making them a top choice for entryways. Fiberglass doors balance durability with aesthetic versatility, often mimicking wood textures while requiring less maintenance.
How to Install a Door
Installing a door requires precision, preparation, and the right tools to ensure a professional finish. Whether you are working with prehung doors, slab doors, or specialty doors like barn doors, having the appropriate equipment is crucial.
Depending on the door type, installation typically takes 1-3 hours for prehung or slab doors and up to 4 hours for more complex installations like sliding or barn doors.
Tools Needed:
- Measuring Tape: For accurate measurements of the door frame and door itself.
- Level: Ensures the door and frame are properly aligned and plumb.
- Hammer or Drill: Used for securing hinges and screws.
- Screwdriver Set: For attaching or adjusting hinges and hardware.
- Chisel: Helps create recesses for hinges when installing slab doors.
- Circular Saw or Jigsaw: To trim the door if adjustments are necessary.
- Shims: Used to level and stabilize the door during installation.
- Utility Knife: For cutting weatherstripping or shims as needed.
- Caulking Gun and Sealant: For exterior door installations to ensure a weatherproof seal.
- Pencil: For marking hinge and hardware positions.
Prehung Door Installation
- Prepare the Opening: Ensure the door frame is clean and leveled. Remove old door components if necessary.
- Insert the Prehung Unit: Place the prehung door (with its frame) into the opening and shim it for alignment.
- Secure the Frame: Nail or screw the frame into place, starting with the top corners. Check for level and plumb as you work.
- Finish with Trim: Install casing around the frame to conceal gaps.
Slab Door Installation
- Fit the Door: Align the slab within the existing frame and mark hinge and lock positions.
- Attach Hinges: Chisel hinge recesses into the door edge and frame. Screw hinges into place.
- Install Hardware: Drill and install the doorknob and lockset.
Sliding Patio Door Installation
- Assemble the Frame: Attach the sliding door frame components as per manufacturer instructions.
- Install the Frame: Fit the frame into the opening and secure it with screws.
- Add Door Panels: Insert the fixed panel first, then the sliding panel, adjusting rollers for smooth operation.
Barn Door Installation
- Install the Track: Mount the track above the door frame securely with screws.
- Attach Rollers: Screw rollers onto the door's top edge.
- Hang the Door: Lift the door onto the track and ensure it rolls smoothly. Add door stops and guides for stability.
Storm Door Installation
- Measure and Prep: Confirm the storm door size matches the opening. Install the door frame pieces and align them.
- Secure the Door: Attach the storm door to the frame with hinges, ensuring it opens and closes properly.
- Add Accessories: Install the door closer, latch, and optional screens.
Door Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures your doors remain functional and visually appealing for years. Here are key tips for maintaining various types of doors:
- Entry Doors: Clean with a non-abrasive solution and inspect for signs of rust, weather damage, or peeling paint. Reapply weatherstripping and sealant annually to maintain insulation.
- Patio Doors: Regularly clean glass panels with glass cleaner and check sliding tracks for debris. Lubricate the track and hinges to ensure smooth operation.
- Interior Doors: Dust and clean periodically, and tighten or adjust hinges if doors begin to sag or squeak. For solid wood doors, inspect for cracks and refinish as needed.
- Storm Doors: Keep the glass or screen panels clean and lubricate moving parts like retractable screens and hinges. Inspect seals and replace them if worn.
How to Choose the Right Door
Selecting the right door involves several factors that ensure functionality, durability, and style alignment with your needs. Below are key considerations to guide your decision:
Purpose and Function
Choose a door that fits its intended use—entry doors for security, patio doors for connectivity, or interior doors for privacy. Matching functionality with design ensures optimal performance.
Material
The material impacts durability, maintenance, and cost. Wood offers timeless charm, fiberglass excels in low maintenance, and steel ensures top-notch security.
Style and Design
Align door styles with your home’s decor. Decorative glass, panels, or minimalist finishes can complement various architectural themes.
Energy Efficiency
For exterior doors, insulation and thermal performance are critical. Look for fiberglass or steel options with insulated cores to reduce energy costs.
Door FAQs
What’s the difference between a prehung door and a slab door?
Prehung doors include the frame and hinges, while slab doors are just the panel.
How do I choose the right material?
Consider durability, maintenance, and location. For instance, fiberglass is low-maintenance and weather-resistant.
What style is best for modern homes?
Sliding or French patio doors and minimalist panel entry doors suit contemporary designs.
Can I customize my entry or patio door design?
Yes, most door manufacturers offer customization options, including material, color, hardware, and glass panel designs. This allows you to tailor the door to match your home’s architectural style and personal preferences.
How do I maintain my storm door for long-lasting performance?
Regularly clean the glass or screen, lubricate the hinges, and check for wear on the weatherstripping. For retractable screens, ensure they retract smoothly and avoid forcing the mechanism.
What factors should I consider when choosing a patio door?
Key considerations include space constraints, material durability, desired aesthetics, and energy efficiency. For example, sliding doors are great for tight spaces, while French doors add elegance but require more room to open.
Get Started with LS Building Products
Enhance your project with our extensive selection of doors. From elegant entry doors to functional interior designs, LS Building Products provides the perfect solutions tailored to your needs.
Contact us today to explore our products and services or schedule a consultation with our experts!
.png?width=98&height=67&name=Logo%20(13).png)
.jpg) Door Terminology: A Glossary Page for Understanding Doors" loading="lazy">
Door Terminology: A Glossary Page for Understanding Doors" loading="lazy">






.jpg)